According to a recent World Health Organization Report, one in four people are at risk of poor health due to inactivity. The WHO defines inactive as those who did less than 150 minutes of moderate exercise – or 75 minutes at vigorous intensity – a week. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to chronic health problems such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Not surprisingly, people are less active than before, what is surprising is that since 2001, despite our best efforts the rate of inactivity has not changed. Wealthier countries such as Canada, the United States, and the UK were found to be more inactive than developing countries. Consider this chart prepared by the BBC:
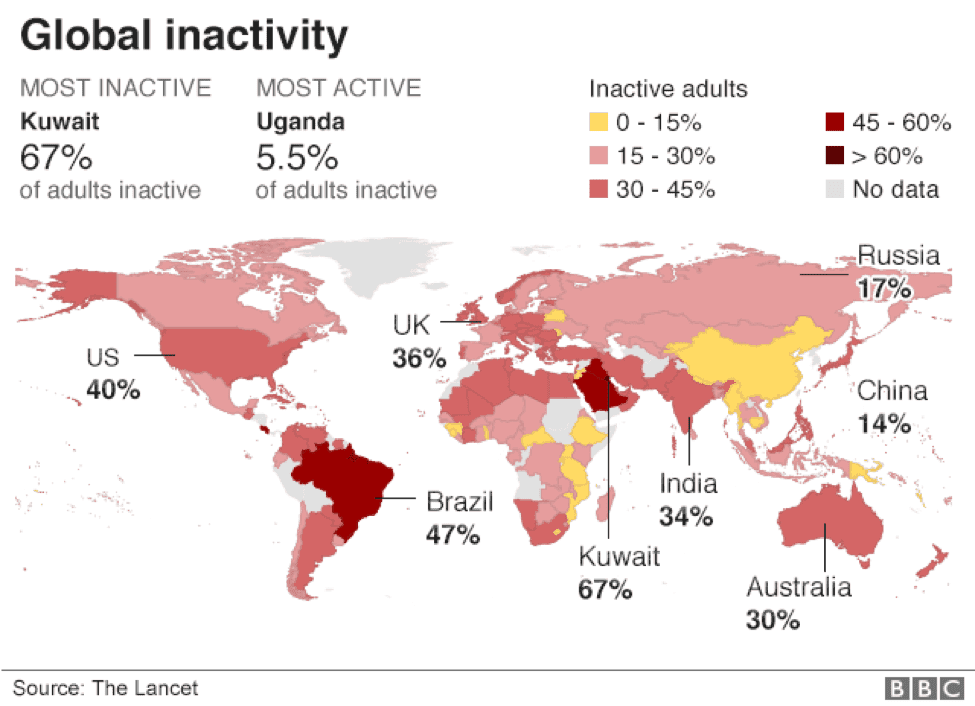
With the increase in childhood obesity, cardiovascular disease anddiabetes, maintaining an active lifestyle is paramount to a healthy lifestyle.
What can you do to help reduce your risks? The WHO recommends following these activity guidelines:
Exercise guidelines for 19- to 64-year-olds
How much?
- At least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity every week
- Strength exercises on two or more days a week that work all the major muscles
- Break up long periods of sitting with light activity
What is moderate aerobic activity?
- Walking fast, water aerobics, riding a bike on level ground or with a few hills, doubles tennis, pushing a lawn mower, hiking, skateboarding, rollerblading, volleyball, and basketball
What counts as vigorous activity?
- Jogging or running, swimming fast, riding a bike fast or on hills, singles tennis, football, rugby, skipping rope, hockey, aerobics, gymnastics, and martial arts
What activities strengthen muscles?
- Lifting weights, working with resistance bands, doing exercises that use your ownbody weight, such as push-ups and sit-ups, heavy gardening, such as digging and shovelling, and yoga
What activities are both aerobic and muscle-strengthening?
- circuit training, aerobics, running, football, rugby, netball, hockey
Source: NHS
For more information on activity related guidelines, click here:https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/exercise/


Write Reviews
Leave a Comment
No Comments & Reviews