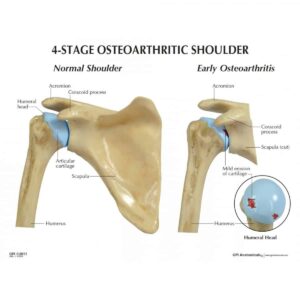
 Arthritis usually refers to the breakdown of cartilage within a joint that can potentially cause a lot of pain and discomfort for those who experience it, it is a broad term that describes hundreds of different joint related issues. Shoulder arthritis refers directly to a lack of cartilage within the glenohumeral joint, a joint that connects the ball-like proximal end of your humerus to the socket of your shoulder. Shoulder arthritis can also potentially occur in the acromioclavicular joint (AC joint), another joint located in the shoulder which is more common in people aged 50+. This deterioration of the cartilage is called osteoarthritis or “wear and tear” arthritis which causes a painful sensation due to the unwanted bone-on-bone contact within the joint. Other potential causes of arthritic pain in the shoulder include:
Arthritis usually refers to the breakdown of cartilage within a joint that can potentially cause a lot of pain and discomfort for those who experience it, it is a broad term that describes hundreds of different joint related issues. Shoulder arthritis refers directly to a lack of cartilage within the glenohumeral joint, a joint that connects the ball-like proximal end of your humerus to the socket of your shoulder. Shoulder arthritis can also potentially occur in the acromioclavicular joint (AC joint), another joint located in the shoulder which is more common in people aged 50+. This deterioration of the cartilage is called osteoarthritis or “wear and tear” arthritis which causes a painful sensation due to the unwanted bone-on-bone contact within the joint. Other potential causes of arthritic pain in the shoulder include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- The synovium is a very thin layer of connective tissue present at every joint to help lubricate and facilitate movement smoothly. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that usually occurs in both shoulders at the same time, causing the body to attack/damage its own healthy cells (ex. Bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments) and swelling of the synovium.
- Post-traumatic shoulder arthritis
- A term that simply refers to arthritic symptoms developed because of a previous shoulder injury (ex. Dislocation, fracture etc.).
- Avascular necrosis
- A condition that disrupts the supply of blood to a given location, causing the cells within the bone to die and the bone itself to gradually collapse unevenly. As the bone breaks down and end of the humerus loses its sphere-like shape the joint will not rotate smoothly as it is meant to causing problems within.
- Potential causes include: heavy alcohol use, steroids, or sickle cell anemia.
Symptoms:
- pain/discomfort
- Usually said to be felt “deep” within the joint but may sometimes radiate down to the elbow and wrist in severe cases.
- May intensify with changes in weather conditions
- Loss of motion
- Stiffness
- Decrease in range
- Grinding sensation
- Sliding sensation
- Often “locks up”
 Arthritis usually refers to the breakdown of cartilage within a joint that can potentially cause a lot of pain and discomfort for those who experience it, it is a broad term that describes hundreds of different joint related issues. Shoulder arthritis refers directly to a lack of cartilage within the glenohumeral joint, a joint that connects the ball-like proximal end of your humerus to the socket of your shoulder. Shoulder arthritis can also potentially occur in the acromioclavicular joint (AC joint), another joint located in the shoulder which is more common in people aged 50+. This deterioration of the cartilage is called osteoarthritis or “wear and tear” arthritis which causes a painful sensation due to the unwanted bone-on-bone contact within the joint. Other potential causes of arthritic pain in the shoulder include:
Arthritis usually refers to the breakdown of cartilage within a joint that can potentially cause a lot of pain and discomfort for those who experience it, it is a broad term that describes hundreds of different joint related issues. Shoulder arthritis refers directly to a lack of cartilage within the glenohumeral joint, a joint that connects the ball-like proximal end of your humerus to the socket of your shoulder. Shoulder arthritis can also potentially occur in the acromioclavicular joint (AC joint), another joint located in the shoulder which is more common in people aged 50+. This deterioration of the cartilage is called osteoarthritis or “wear and tear” arthritis which causes a painful sensation due to the unwanted bone-on-bone contact within the joint. Other potential causes of arthritic pain in the shoulder include: